Mobile robot navigation using Reinforcement Learning
So far, I have spent more than a week learning to work with the Deepbots framework, which helps to communicate Webots simulator with reinforcement learning algorithm training pipeline. This time the task was to teach a robot to navigate to any point in a workspace. Firstly, I decided to implement a navigation using only a discrete action space to get used to the working with RL, and will eventually switch to a continuous action space.
Through multiple iterations, I have come up with the following space dimensions:
- Observation space: 34 (2 position, 2 velocity, 30 laser)
- Action space: 4 (forward, turn left and right, stop)
For training I have used the Proximal Policy Optimization algorithm (again) with the following actor-critic network design, inspired by [2]:
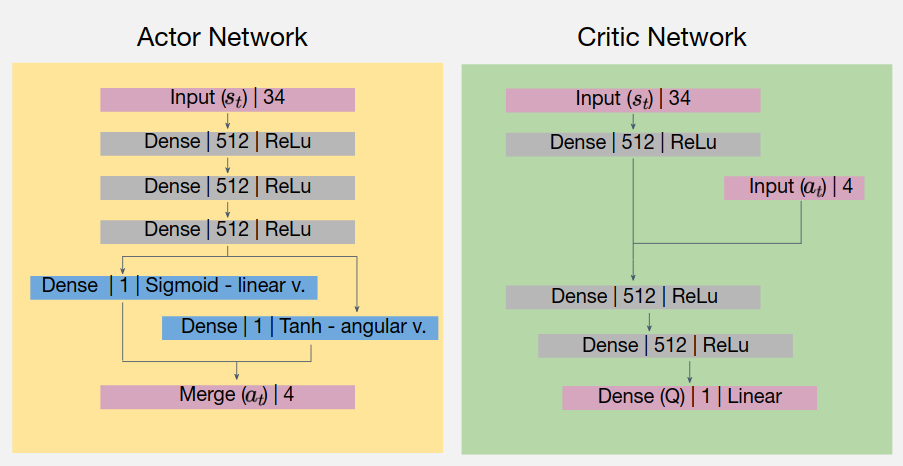
However, the most challenging part was the reward shaping. I’ve read a lot of papers reagarding mobile robot navigation using reinforcement learning, and implemented multiple of them, but with no success. The most notable case, for example, was the following navigation policy (I call it dancing robot policy):
The task was to reach a point with yellow ball, but robot is moving close to it (never actually reaching it, which will end the episode), to gather more dense rewards. This as a result gives a very strange kind of motion.
Finally, I used the reward model used by [2]:
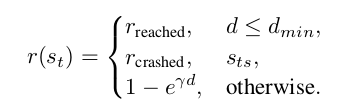
This reward shaping allowed to train the robot to reach a final destination in a very nice way, and took around 2 hours. The deployment of the generated policy is shown below:
The next task would be to train the robot to reach varying points (any) in the workspace, but it would definitely take much more time and compute resources.
[1] Tai, Lei, Giuseppe Paolo, and Ming Liu. “Virtual-to-real deep reinforcement learning: Continuous control of mobile robots for mapless navigation.” 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). IEEE, 2017.
[2] Botteghi, Nicolò, et al. “On Reward Shaping for Mobile Robot Navigation: A Reinforcement Learning and SLAM Based Approach.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.04109 (2020).
